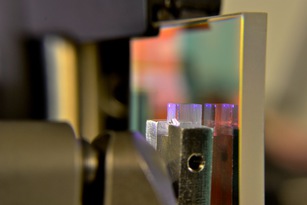
Micro-mirror test setup
These are two ultra-high reflectivity mirrors for the wavelength bands 390-425nm and 800-860nm that we used for preparing a strongly-coupled cavity to single-strontium ions. You can see several blue-spots at the corner of the small piece of glass, this is an incident 422nm laser beam used to test the cavity formed by the two mirrors.
This thesis is organized in three parts. The first consists of an introduction to the theory and methods used in ion trap systems. This includes descriptions of the trapping principles used in surface-electrode Paul traps, level-structure for our ion of choice - strontium - with motional degrees of freedom, and description of the protocols used for quantum-state manipulation. The second part of this thesis contains descriptions of the theory and construction experimental hardware developed during the course of this work. The last part consists of the experiments performed throughout this thesis with an emphasis on the protocols developed for parallel quantum logic gates and matter-wave interferometry.
A rough layout of content will be as follows.
Part I
On Paul traps
- linear paul trap
- conformal mapping and scaling coeff
- micromotion intrinsic and excessive
- psuedo-potential and the harmonic oscillator
- surface trap control
- multipole expansion
- transport
On Atom - light interactions
- two-level atom: lifetime, rabi, stark shifts
- three-level atom: zeeman-levels, dark-states, recycling
- Strontium level structure
- atomic motion coupling, laser cooling
On Quantum state manipulation
- spin-state intialization
- motional-state intialization
- sigmax rotations
- sigmaz rotations
- spin-motion entangling
- molmer-sorensen
- POVM’s
Part II
Control theory
Optical reference cavities
- octablock
- ULE
Laser systems
- doubling cavity 844-422
- 1092
- 1033
- 405 + 461
- 674
Experiment optics
- distribution optics
- PCF assembly
- experiment beam geometries
- beam injection setup
- imaging lenses
Vacuum system
- experiment flange + chamber optics
- wiring
- oven
- pumping system: chamber conductance
QuAcq
- MTserver
- Jarvis
- QuACK
- hardware
Part III
diagnostic: in-loop experiment signals
include measurements
- Doppler
- micromotion
- fluorescences detection
- S-D spectrum
- D-lifetime
- Rabi progression
- Ramsey
- Ramsey lock
- Power lock
- Pi-time stabilization
- Stark shifts
- beam pointing adjustment
- Gate set
- laser-phase tomography
- position-phase tomography
- ion transport
Position-controlled quantum logic gates
- scaling problems
- phase control
- composite quantum logic gates design
- demonstration of position controlled arbitrary logic gate
- demonstration of independent parallel logic gates
- tomography
Matter-wave interferometry
- prior art
- phase sensitivity
- extended frequency range
- squeezing
metrology architecture
- prior work: single ions
- extending to multi-site multi-ion systems
- tiled architecture, propose system size